Data Journalism
Data Journalism Top 10: Celebrity Jets, Amazon Destruction, Pakistan Floods, Meme Origins
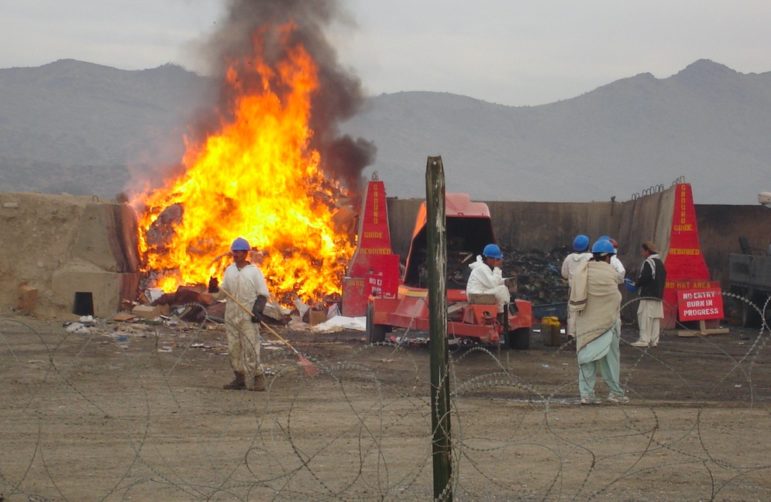
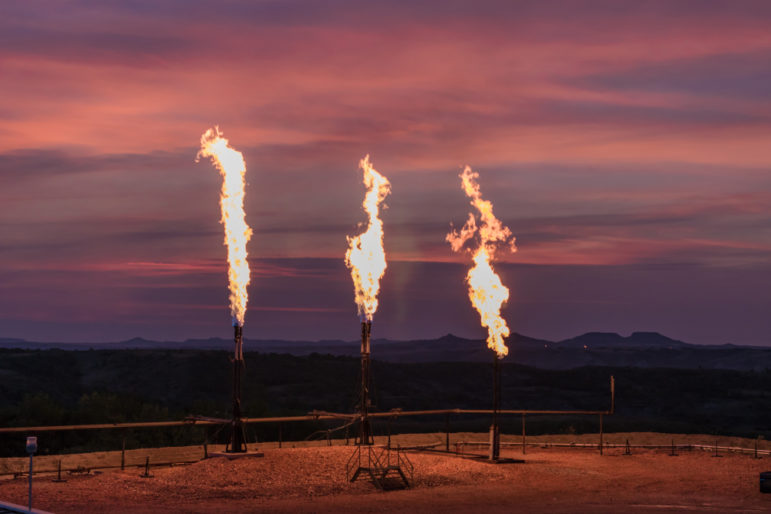
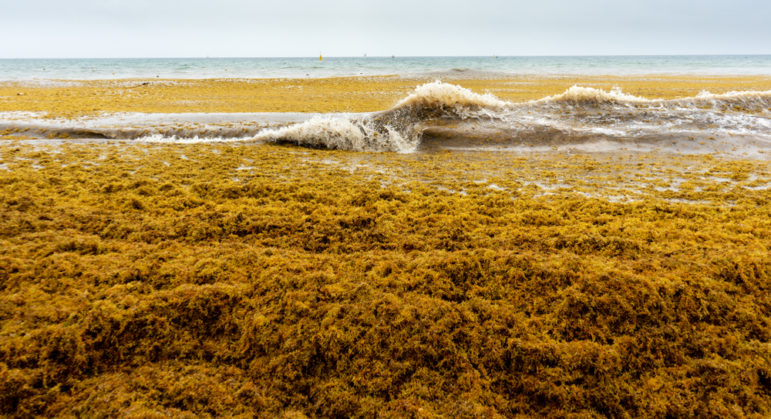
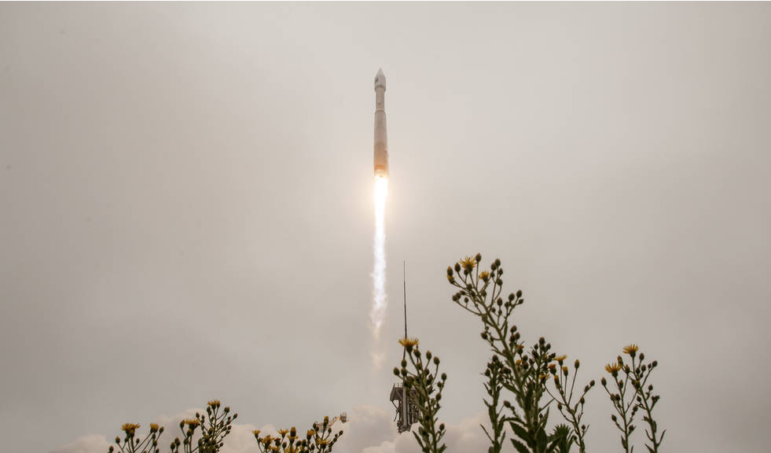
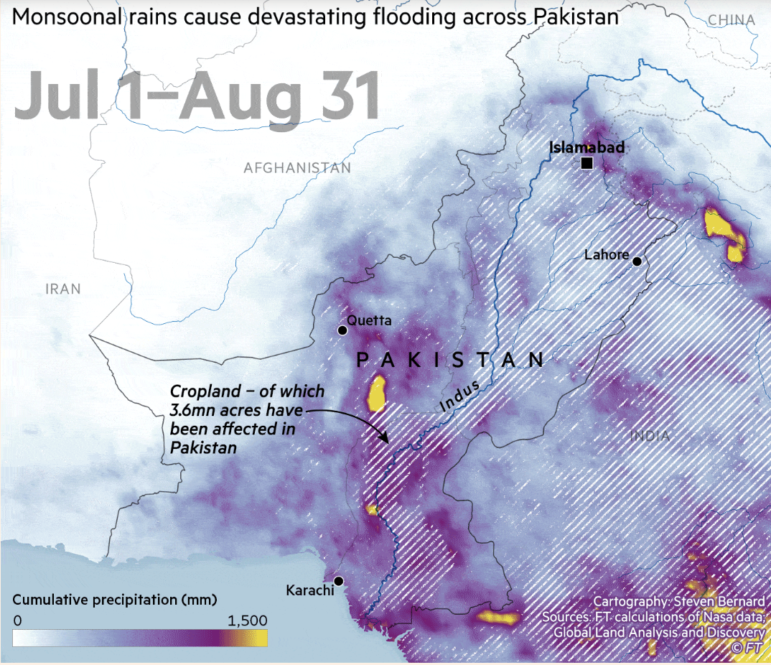
This week’s Top 10 in Data Journalism features the carbon footprint of celebrity jets, the unsanctioned destruction of the Amazon, secret documents seized from Trump, massive Pakistan flooding, and a look into the history of memes.









